I recommend Zapier for businesses and individuals seeking to automate repetitive tasks without coding knowledge. Zapier connects over 7,000 applications through an intuitive interface, significantly boosts productivity, and offers scalable plans starting from free. However, the platform has limitations including a steep learning curve for complex workflows, potential costs that increase with usage, and occasional reliability issues with certain integrations.
Understanding Zapier’s Automation Power
Zapier functions as a powerful no-code automation platform that connects your favorite apps and services. The platform enables users to create automated workflows called “Zaps” that trigger actions between different applications.
Users can automate repetitive tasks such as transferring data between applications, sending notifications, or updating records across multiple platforms. This automation capability saves significant time and reduces manual effort in daily operations.
The platform works through a trigger-action model where an event in one application initiates predetermined actions in other connected applications. This simple concept allows for powerful automation scenarios across your digital ecosystem.
Recent 2025 updates have introduced AI-powered enhancements that provide smart workflow suggestions and improved decision-making capabilities. These features further optimize the automation process and make Zapier more intuitive to use.
Key Features and Capabilities
Zapier offers several powerful features that make it a standout automation tool in 2025. The platform’s extensive app integration library allows you to connect virtually any business or productivity tool in one seamless system.
The trigger-based automation system can initiate workflows based on specific events, such as receiving an email, adding a calendar event, or updating a database record. This event-driven approach ensures your workflows remain responsive to real-time changes.
Multi-step Zaps enable complex workflow creation where a single trigger can initiate multiple actions across different applications. This capability allows for sophisticated automation scenarios that would otherwise require custom programming.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 7,000+ App Integrations | Connect tools like WordPress, Google Docs, and social media platforms | Build end-to-end workflows across multiple platforms |
| Multi-Step Zaps | Create complex workflows with multiple actions from a single trigger | Automate sophisticated business processes |
| Filters & Conditionals | Add logic to workflows to process only relevant information | Create smarter, more targeted automations |
| Formatting | Transform data between apps to ensure compatibility | Seamless data transfer between different platforms |
| Error Handling | Automatic retry for failed Zaps | Improved reliability for critical workflows |
Filters and conditional logic allow users to create more sophisticated workflows that only execute under specific conditions. This feature prevents unnecessary actions and ensures automation occurs only when relevant.
Data transformation capabilities ensure information passes correctly between different applications with varying data formats. This functionality proves essential when connecting systems with different field requirements or naming conventions.
Setting Up Your First Zap
Creating your first automation with Zapier requires a methodical approach to ensure all components work together seamlessly. The process begins with account creation and basic familiarization with the platform interface.
New users should start by visiting Zapier.com and signing up for an account, with options ranging from the free plan to more advanced paid tiers. The free plan offers 100 tasks per month, sufficient for testing basic workflows.
After account creation, the next step involves designing your first Zap by clicking the “Create Zap” button on your dashboard. This action opens the Zap editor where you’ll construct your automation.
Building a Basic Workflow
The foundation of any Zap begins with selecting appropriate triggers and actions. Triggers determine when your workflow executes, while actions define what happens during execution.
A typical workflow might start with a trigger such as “New Email in Gmail” and connect to an action like “Create Card in Trello.” This simple automation would create a new Trello card whenever you receive an email matching your specified criteria.
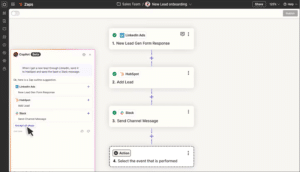
The next step involves configuring your trigger by connecting to the relevant account and specifying trigger conditions. Zapier guides you through this process with clear instructions and testing options.
| Workflow Stage | Example | Configuration Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger Selection | New form submission, email received, calendar event | Choose specific triggers relevant to your workflow |
| Account Connection | Connect to Gmail, Trello, Slack, etc. | Use secure OAuth connections for better security |
| Filter Setup | Only process emails with attachments | Add conditions to make automations more precise |
| Action Configuration | Create Trello card, send Slack message | Map fields carefully between trigger and action |
| Testing | Send test data through the workflow | Verify all steps work before activating |
After configuring your trigger, you’ll set up the corresponding action by connecting to the destination application and mapping data fields. This mapping tells Zapier which information should transfer from the trigger to the action.
Testing represents a crucial step before activating your Zap. Zapier provides testing tools that simulate the workflow with sample data, allowing you to verify correct operation before going live.
Once testing confirms proper functionality, you can activate your Zap with a simple toggle switch. The automation will now run automatically whenever the trigger conditions are met.
Advanced Zapier Techniques
Experienced Zapier users can implement more sophisticated automation techniques that enhance productivity and workflow efficiency. These advanced approaches leverage the platform’s flexibility and powerful features.
Path branching allows workflows to take different actions based on specific conditions. For example, a new customer form submission might route to different departments based on the product interest indicated.
Nested Zaps create more complex automation systems where the completion of one Zap triggers another. This capability enables building comprehensive automation ecosystems that handle multi-stage business processes.
| Advanced Technique | Implementation Method | Use Case Example |
|---|---|---|
| Path Branching | Use Paths feature to create conditional workflows | Route support tickets to different teams based on priority |
| Delay Steps | Add timed delays between actions | Send follow-up emails 3 days after initial contact |
| Lookup Tables | Use spreadsheets to map values between systems | Convert product codes between inventory and accounting systems |
| Formatter | Transform data using built-in formatting tools | Convert dates between different formats for compatibility |
| Webhooks | Connect to custom APIs or unsupported applications | Integrate with proprietary internal systems |
Delay steps introduce timed pauses between actions, allowing for sequences that require specific timing. This feature proves valuable for follow-up communications or staged process implementation.
Lookup tables enable mapping between different value systems, such as converting category names between platforms or translating status codes. This capability ensures consistent data across systems with different terminology.
Custom webhooks extend Zapier’s capabilities to applications without native integrations. This advanced feature allows connections to internal systems or specialized tools through standard API calls.
Real-World Zapier Applications
Successful implementations of Zapier demonstrate the platform’s versatility and effectiveness across various business functions. These real-world examples provide practical insights for your own automation projects.
Marketing teams use Zapier to streamline lead management by automatically transferring form submissions to CRM systems and triggering follow-up email sequences. This automation ensures prompt response to potential customers and consistent lead nurturing.
Customer support operations benefit from automations that route support tickets, send acknowledgment messages, and update internal tracking systems. These workflows improve response times and ensure consistent customer communication.
| Business Function | Automation Example | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Marketing | Form submissions → CRM → Email sequence | Faster lead response, consistent follow-up |
| Sales | Deal updates → Team notifications → Document generation | Improved team coordination, reduced admin work |
| HR | Application received → Background check → Interview scheduling | Streamlined hiring process, better candidate experience |
| Finance | Invoice received → Approval workflow → Payment processing | Faster processing, reduced manual data entry |
| Operations | Inventory alerts → Purchase orders → Supplier notifications | Proactive inventory management, reduced stockouts |
Sales teams implement Zaps that notify team members of deal progress, update forecasting spreadsheets, and generate contracts automatically. These automations reduce administrative overhead and keep teams focused on selling.
Human resources departments automate candidate processing workflows that manage applications, schedule interviews, and send onboarding materials. These systems improve hiring efficiency and provide better candidate experiences.
Finance operations leverage Zapier to connect accounting systems, payment processors, and approval workflows. These automations reduce manual data entry and accelerate financial processes.
Zapier vs. Competitors
When comparing Zapier to alternatives for business automation, several key differences emerge. These distinctions help determine which platform best suits your specific needs and technical requirements.
Microsoft Power Automate offers deeper integration with Office 365 but comes with a steeper learning curve and higher enterprise pricing. Zapier provides better value for small to medium businesses not heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Make.com (formerly Integromat) provides more visual workflow building with a flowchart-style approach compared to Zapier’s more linear workflow structure. Zapier offers a more straightforward experience for beginners, while Make.com provides greater flexibility for complex workflows.
| Feature | Zapier | Power Automate | Make.com | IFTTT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing (Basic) | $19.66/month | €14/user/month | $9/month | $5/month |
| App Integrations | 7,000+ | 1,000+ | 1,000+ | 700+ |
| Ease of Use | High | Moderate | Moderate | Very High |
| Complex Workflows | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Limited |
| Free Plan | 100 tasks/month | Limited features | 1,000 ops/month | 5 applets |
IFTTT (If This Then That) offers simpler automation with a focus on personal and smart home applications. Zapier provides more business-oriented features and supports more complex workflows than IFTTT’s straightforward approach.
Pricing structures differ significantly, with Zapier’s costs increasing based on the number of tasks and active Zaps. Power Automate uses a per-user model, while Make.com and IFTTT offer more operations per dollar at lower tiers.
The choice between these platforms often depends on specific requirements, existing technology investments, and the complexity of desired automations. Zapier excels for businesses seeking a balance of power and usability without extensive technical expertise.
Zapier Pricing and Plans
Zapier offers a range of pricing tiers designed to accommodate different automation needs and budgets. The pricing structure is based primarily on the number of tasks (individual automated actions) and active Zaps (automation workflows).
The Free plan provides a starting point with 100 tasks per month and single-step Zaps. This tier allows new users to explore basic functionality without financial commitment.
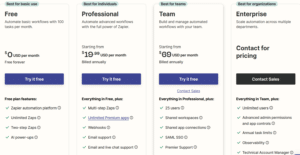
Paid plans begin with the Starter tier at approximately $19.66 per month, offering 750 tasks and multi-step Zaps. This level suits small businesses or individuals with moderate automation needs.
| Plan | Monthly Price | Tasks | Active Zaps | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 100 | 5 | Single-step Zaps, 5-minute update time |
| Starter | $19.66 | 750 | 20 | Multi-step Zaps, 3 Premium Apps |
| Professional | Higher | 2,000 | Unlimited | Paths, Custom Logic, Autoreplay |
| Team | Higher | 50,000 | Unlimited | Shared workspaces, Premier support |
| Company | Custom | Custom | Unlimited | Advanced admin, Enterprise support |
The Professional plan increases task limits to 2,000 per month and adds advanced features like Paths for conditional workflows and Autoreplay for failed tasks. This tier suits businesses with more sophisticated automation requirements.
Team and Company plans cater to larger organizations with higher task volumes and collaboration needs. These tiers include features like shared workspaces, user permissions, and advanced support options.
All paid plans include features like multi-step Zaps and faster update times, with higher tiers adding more sophisticated capabilities like custom logic, error handling, and advanced admin controls.
Best Practices for Zapier Success
Implementing effective automation with Zapier requires adherence to certain best practices that maximize efficiency and reliability. These guidelines help avoid common pitfalls and optimize your automation investment.
Start with simple workflows that automate one specific pain point in your process. This incremental approach allows for testing and refinement before tackling more complex automations.
Document your Zaps thoroughly with clear naming conventions and descriptions. This practice facilitates troubleshooting and allows team members to understand and modify automations when necessary.
Regular monitoring and optimization keep your automations performing efficiently. Schedule periodic reviews to identify bottlenecks or errors and refine your workflows accordingly.
Test your Zaps thoroughly before full implementation, using sample data to verify all steps execute correctly. This validation process prevents potential issues when deploying to your actual business processes.
Implement error handling strategies like notification alerts for failed Zaps and the Autoreplay feature for critical workflows. These precautions help maintain business continuity when issues arise.
My Experience with Zapier
After implementing Zapier across several business functions, I’ve observed significant improvements in both efficiency and output quality. The platform’s flexibility accommodates various workflows while maintaining reliability for critical processes.
The learning curve presents the primary challenge, particularly for complex scenarios with multiple conditional paths. However, the visual interface makes the learning process more intuitive than code-based alternatives.
Cost-effectiveness remains a standout advantage for small to medium businesses, with our automation costs averaging $20-30 monthly while saving approximately 20-30 hours of manual work. This return on investment justifies the subscription expense many times over.

The most successful implementations combine automated data transfer with notification systems that keep team members informed. This hybrid approach maintains human oversight while eliminating repetitive tasks from the workflow.
Integration reliability varies between applications, with mainstream services like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 performing exceptionally well, while some niche applications occasionally experience connection issues. This variability requires consideration when planning critical automations.
FAQ
Q: How much does Zapier cost in 2025?
A: Zapier offers several pricing tiers in 2025, starting with a free plan that includes 100 tasks per month and 5 single-step Zaps. The Starter plan costs approximately $19.66 per month for 750 tasks and 20 active Zaps with multi-step capabilities. Higher tiers include Professional, Team, and Company plans with increased task limits and advanced features. Pricing increases based on the number of tasks and active Zaps needed.
Q: Can Zapier completely automate my business processes?
A: While Zapier can automate significant portions of your business processes, complete automation without human oversight isn’t recommended for most scenarios. The platform works best for repetitive, rule-based tasks like data transfer, notifications, and standard workflows. Complex decisions, creative work, and situations requiring judgment still benefit from human involvement. A hybrid approach where Zapier handles routine tasks while humans manage exceptions and strategic elements typically yields the best results.
Q: How difficult is it to learn Zapier?
A: Zapier presents a moderate learning curve that varies based on your technical background and the complexity of your desired workflows. Basic Zaps can be mastered within a few hours using the platform’s intuitive interface and templates. More complex automations with conditional logic and multiple steps might require several days of practice. The platform provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and a helpful community to support the learning process.
Q: What are the limitations of using Zapier?
A: Zapier has several limitations to consider: task limits based on your subscription tier, a 5-15 minute delay between trigger and action on lower plans, and dependency on third-party API stability. Additionally, complex workflows may become difficult to troubleshoot, and costs can increase significantly as you add more automations. Some users also report occasional reliability issues with certain integrations, particularly with less common applications or during API changes.
Q: Can Zapier integrate with custom or internal applications?
A: Yes, Zapier can integrate with custom or internal applications through its Webhooks feature. Webhooks allow you to connect Zapier to any system with an accessible API, even if there’s no native integration. For more advanced needs, Zapier offers a Developer Platform that allows creating custom integrations. These options require some technical knowledge but enable connecting Zapier to proprietary systems, legacy applications, or specialized tools not available in the standard integration library.
Q: How does Zapier handle sensitive data and security?
A: Zapier implements several security measures to protect sensitive data, including encryption in transit and at rest, SOC 2 Type II compliance, and regular security audits. The platform allows setting user permissions and access controls on Team and Company plans. However, users should be aware that data passes through Zapier’s servers during automation, so sensitive information should be handled according to your organization’s security policies. For highly regulated industries, reviewing Zapier’s security documentation and possibly implementing additional safeguards is recommended.


